Which of the Following Countries Has Achieved Replacement-level Fertility
What would happen if every country in the world achieved below-replacement fertility rates. The total fertility rate decreased as a result of a delay in age of first marriage and increased contraceptive use.
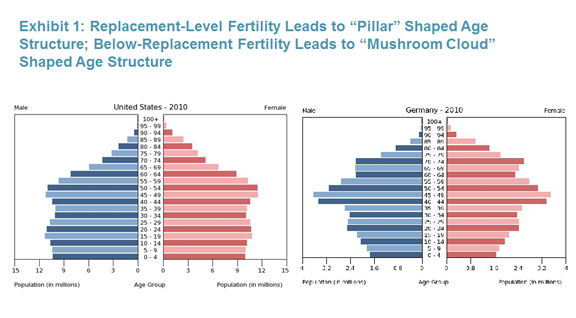
Fertility Rates And Age Structures The Underpinnings Of Replacement Fertility In The U S Joint Center For Housing Studies
In developed countries replacement level fertility can be taken as requiring an average of 21 children per woman.

. Yet countries such as Botswana and Rwanda have demonstrated that enormous progress is possible. A newly published study has found that nearly half of countries have fertility rates which are below replacement level meaning that population size will decrease without immigration. 204 rows Replacement fertility is the total fertility rate at which women give.
A level of reproduction in which a population exactly replaces itself from one generation to the next. Singapore Hong Kong and South Korea. Already in the 1968 Revision the medium- variant projection for Japan kept its fertility levels slightly below replacement level.
A 17 b21 c. What is replacement-level fertility in highly developed countries. All of the following countries achieved replacement-level fertility within 15-30 years except.
Asked Jun 26 2020 in Sociology by Cristal. Achieving replacement level fertility in Sub-Saharan Africa and elsewhere by 2050 is a multi-win solution to humanitarian economic and environmental challenges and an important item on the menu for a sustainable food future. If the growth rate remains constant in approximately how many years will the population be closest to 1 billion.
The provisional Census 2011 figures show that all four south Indian States Andhra Pradesh Karnataka Kerala and Tamil Nadu have already achieved the replacement level fertility of 21 children per women required to initiate the process of population stabilization while the four large north Indian States Bihar Madhya Pradesh Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh. In developed countries replacement level fertility can be taken as requiring an average of 21 children per woman. Have total fertility rates TFR well below replacement level 1-6 and 1-5 respectively.
Life expectancy is 12 years higher than India. The total fertility rate in country A was 68 in 1980. The current global human population is about 61 billion and is growing at an annual rate of 135 percent.
All of the following countries achieved replacement-level fertility within 15-30 years. B Rwanda and Zambia are most likely experiencing population decline. Ential articles have drawn attention to a slowdown of fertility declines in the last decade3 The only developing countries to have achieved replacement-level fertility are the newly industrialized nations of East Asia-Hong Kong Singapore South Korea and Taiwan.
A country currently has a population of 250 million and an annual growth rate of 25. How many countries have achieved below-replacement fertility rates. That level of reproduction in which a mother delivers a single daughter.
Which of the following statements best supports the change in the total fertility rate in country A. The fertility transitions of Cuba and Korea were achieved through high rates of contraceptive prevalence and ready access to legal abortion. The consensus is that Chinas fertility rate has dropped to a level below replacement and its economic growth has increased the per capita standard of living of its citizens by more than fourfold due to its one child policy.
Which of the following is a true statement about replacement-level fertility. The distinctive attri-butes of these countries in terms of their. There is enough evidence to prove that there is no population explosion in the country and India has achieved replacement level fertility without the introduction of coercive population policies.
In 2016 all European Union countries had a sub-replacement fertility rate ranging from a low of 13 in Portugal Poland Greece Spain and Cyprus to a high of 20 in France. The countries or areas that have the lowest fertility are in developed parts of East and Southeast Asia. Replacement level fertility and future population growth.
The country with the highest population density is. Population growth would stop and world population would remain stable. The widely accepted replacement level rate is 21 births per female for industrialized countries.
The future fertility levels of countries with very low fertility. Married couples have access to free birth control. The following questions refer to the table below which shows population area and energy use of several countries.
Replacement level fertility is the level of fertility at which a population exactly replaces itself from one generation to the next. If there were no deaths before age 45 then the replacement rate would be 20. Page 15 of 17 A Countries that are larger in total area have higher total fertility rates.
D By 2010 all countries had reached replacement-level fertility rates. The two nations have nearly the same land area but Koreas population is approximately four times the size of Cubas. In countries with high infant and child mortality rates however the average number of births may need to be much higher.
BIt equals the annual number of live births per 1000 people in a population. AIt equals the average number of children a woman will give birth to during her child-bearing years. Illiteracy is about one-third of Indias rate.
Total fertility dropped from 57 to 18 children per woman. C More-developed countries tend to have lower total fertility rates than less-developed countries. Replacement level fertility is the level of fertility at which a population exactly replaces itself from one generation to the next.

Comments
Post a Comment